Georgetown Security Studies Program Alumni Jason Rivera offers some specific but understandable cyber responses. We all throw out some general ideas (I am guilty as charged) but Jason provides some specificity and with his background in cyber he knows what he is talking about.
Note also that Jason has looked at the nexus of cyber war and unconventional warfare. His final paper from the class he took with with me is at footnote 6 below I recommend that unconventional warfare and cyber warfare practitioners take a look at it.
North Korea has crossed the cyber red line by combining cyberattacks with the threat of terrorism – and the United States must respond
A screenshot from the initial cyberattack against Sony. Source: techblogcorner.com
By Jason Rivera
All views and concepts expressed in this article originate solely with the author and do not represent the official positions or opinions of Deloitte & Touche LLP, the US Army National Guard, or the US Department of Defense.
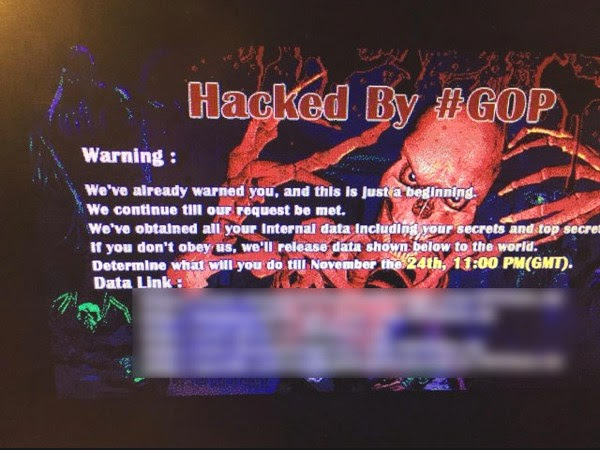
On November 24, 2014, Sony Pictures first received indication that their networks were hacked when a picture of skeletal fingers appeared on the screens of employee computers accompanied by the message stating, “This is just the beginning”.[1] This was followed by a threat to release “top secrets” and sensitive internal data if the film The Interview was released.[2] The Interview is a fictional comedy film directed by Seth Rogan about a couple of journalists who have been instructed by US government officials to assassinate North Korean leader, Kim Jung-un, after landing an interview with him. Over the following weeks, scores of sensitive Sony intellectual property and personal data were released to include four Sony films (most notably, The Interview), personal information about Sony employees, and private emails between top Sony executives. Initially, a hacker group known as the “Guardians of Peace” claimed responsibility for the Sony breach and stated that the breach was in response to Sony’s decision to release The Interview in theaters.[3]
The fact that Sony pictures was breached and the fact that a hacker group sympathetic to North Korea’s political regime is, relative to the history of other cyberattacks against US equities, irrelevant. What is relevant, however, are two revelations that recently surfaced:
- On 17 December 2014, Sony Pictures announced its intent to cancel the 25 December release of The Interview, following a decision made by major movie theater companies to drop the movie.[4]
- Later that same day, it was announced that American intelligence officials have discovered evidence that the North Korean government was “centrally involved” in the recent attacks on Sony Picture’s computers.[5]
At face value, this may not shock a lot of people. It has long been suspected that foreign actors have been targeting US government and economic interests through cyberspace. Some historical cyberattacks and/or cyber breaches by foreign actors include Chinese exfiltration of US intellectual property, Iranian hacking attempts against US military and government officials, and links to Russian hackers in light of the Target and Home Depot breaches. The recently revealed North Korean breach, however, crosses a cyberspace threshold that no other nation has crossed before:
By invoking the memory of 9/11 and by issuing direct threats stating that moviegoers would suffer a “bitter fate”, North Korea has not only conducted a devastating cyberattack, but has combined that attack with the threat of terrorism.
This event represents an important decision point for the United States government. Never before has a cyberattack been successfully combined with the threat of terrorism. Moreover, never before has a cyberattack against the United States critically affected the commercial sector’s decision to exercise its right to free speech as the attack against Sony has. This cyberattack represents the beginning of what could be a slippery slope and, if the United States does not respond, it may be followed by similar tactics used by state and non-state actors throughout the globe. If the United States wishes to prevent what could be a catastrophic cascade of cyberattacks combined with threats of terrorism, then the American nation must respond and it must respond now. Many of us, at this point, are probably thinking of additional sanctions. This, however, will not be enough to deter future attacks using similar tactics.
The United States should deliver a retaliatory response through cyberspace to the North Korean nation. This retaliatory attack should be targeted against North Korean leadership and should transmit a clear signal that the United States will not tolerate cyberattack tactics combined with the use of terrorist threats. Accordingly, the United States should consider response options designed to debilitate the North Korean regime in such a manner as to cause internal instability. Some response options that should be considered are as follows:
- Response Option 1: North Korea’s population lives in abject poverty and is a ruled by a corrupt regime characterize by deeply seeded and fundamentally flawed political beliefs. To prevent the North Korean population from discovering its situation, and thereby rebelling, the North Korean regime completely controls Internet access to its entire population. Given the above, the United States should develop and deploy a cyber capability that can open up externally hosted search engines to the North Korean population that are outside of the jurisdiction of North Korean Internet service providers, thereby hampering the government’s censorship capabilities. The effect of such a capability would enable the North Korean population to have unrestricted access to information and contentious historical events. Such an operation would likely cause internal unrest in North Korea and would serve as a powerful deterrent against future activity.[6]
- Response Option 2: North Korea’s political leaders are well known for their corrupt relationships with organized criminal enterprises. Given this information, the United States should deploy a cyber enabled information operations capability designed to publically expose this relationship to the North Korean population. The United States should deliver this information via any and all information communications technology platforms available to include (but not limited to):
(Continued at the link below)
No comments:
Post a Comment